jQuery 객체 이해하기 (1)
Prototype에 대해 이해했다면, jQuery 객체가 어떤 방식으로 생성되고 사용되는지를 이해하기가 쉬워진다.
이 문서는 jquery-1.2.2.js를 기반으로 설명한다. ( 현재 릴리즈된 버전은 1.5.1 이지만, 구조적으로는 큰 차이를 보이지는 않는다. )
먼저 jQuery function 객체를 생성하는 코드는 다음과 같다.
var jQuery = window.jQuery = function( selector, context ) {
// The jQuery object is actually just the init constructor 'enhanced'
return new jQuery.prototype.init( selector, context );
};만약에 사용자가 $(“<div>”) 로 jquery 객체를 생성한다고 한다면, 제일 처음 위의 함수가 실행될 것이다. 여기서 하는 일이라곤, jQuery.prototype.init을 생성자로 하는 새로운 객체를 생성하여 돌려주는 것이다. jQuery.prototype.init은 다음과 같이 정의된다.
jQuery.fn = jQuery.prototype = {
init: function( selector, context ) {
...............
},jQuery.prototype 에 새로운 객체 {}를 가리키도록 하고 이 {} 안에 각종 property들이 정의된다. 그중 첫번째로 정의되는 property가 init이다. 이 init 함수에서 리턴되는 객체가 결국 $(“<div>“)가 가리키는 객체가 된다.
그렇다면, 이 객체는 어떻게 jQuery.prototype의 각종 property에 접근할 수 있을까?
다음 한줄의 코드가 이러한 의문을 해소시켜준다.
// Give the init function the jQuery prototype for later instantiation
jQuery.prototype.init.prototype = jQuery.prototype;jQuery.prototype.init의 prototype 객체를 jQuery.prototype을 가리키게 함으로써 새롭게 생성된 객체는 jQuery.prototype의 각종 property를 사용할 수 있게된다. 이를 그림으로 표현하면 다음과 같다.
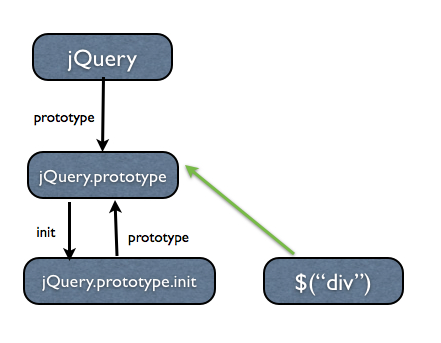
따라서 사용자가 $(“div”)를 통해 생성한 새로운 객체는 jQuery.prototype에 정의되어 있는 여러가지 프로퍼티에 접근할 수 있는 “jQuery” 객체가 되는 것이다.
주의할 점: 사용자가 생성한 객체의 constructor는 jQuery도 아니고, jQuery.prototype.init도 아닌 Object이다.
왜 그럴까? (이 때문에 이후 버전업되면서 jQuery.prototype에 “constructor : jQuery”라는 구문을 추가하여 사용자가 생성한 객체의 constructor가 jQuery임을 명시하였다)
다음에 설명하도록 하겠다.